Utilization of a nitrogen-sulfur nonbonding interaction in the design of new 2-aminothiazol-5-yl-pyrimidines as p38alpha MAP kinase inhibitors.
Lin, S., Wrobleski, S.T., Hynes, J., Pitt, S., Zhang, R., Fan, Y., Doweyko, A.M., Kish, K.F., Sack, J.S., Malley, M.F., Kiefer, S.E., Newitt, J.A., McKinnon, M., Trzaskos, J., Barrish, J.C., Dodd, J.H., Schieven, G.L., Leftheris, K.(2010) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 5864-5868
- PubMed: 20732813
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.07.102
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3NWW - PubMed Abstract:
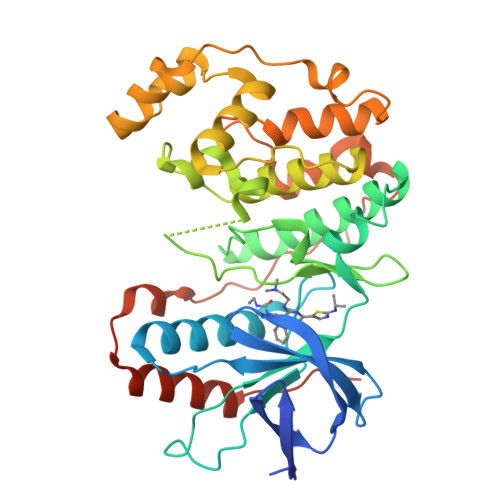
The design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships (SAR) of a series of 2-aminothiazol-5-yl-pyrimidines as novel p38α MAP kinase inhibitors are described. These efforts led to the identification of 41 as a potent p38α inhibitor that utilizes a unique nitrogen-sulfur intramolecular nonbonding interaction to stabilize the conformation required for binding to the p38α active site. X-ray crystallographic studies that confirm the proposed binding mode of this class of inhibitors in p38 α and provide evidence for the proposed intramolecular nitrogen-sulfur interaction are discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Immunology Chemistry, Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceutical Research Institute, Princeton, NJ 08543-4000, USA.